
The X from the mother pairs with both X and Y. The mother carries a XX chromosome and the father carries an XY chromosome. It is now being recently suggested to discontinue the usage of dominant and recessive terms for X-linked inheritance due to highly variable penetrance of X chromosome because of X chromosome inactivation, which is a part of dosage compensation. An affected father’s daughters are all affected as well. The X linked pedigree chart shows that an affected mother and normal father has 50% affected progeny.

In the above case, when someone expresses an X-linked dominant trait, then the person is considered as affected.
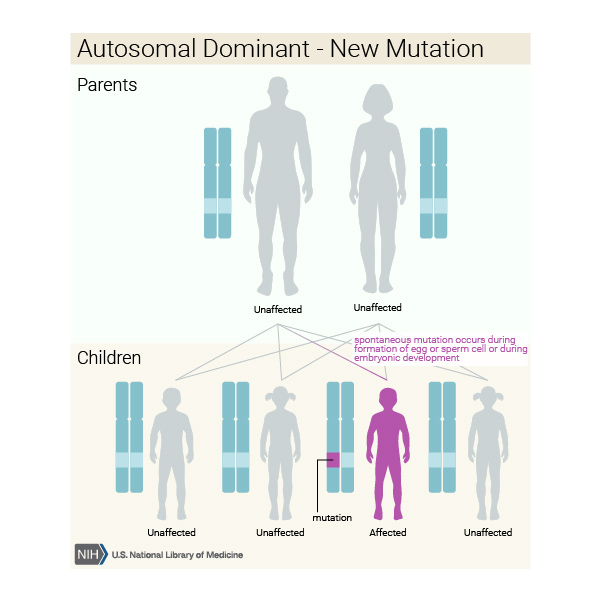

If only allele of the trait specific gene is dominant, then the trait is expressed in the offspring. In the case of X-linked dominant traits, the trait specific gene is located on the X chromosome. This type of inheritance and traits are relatively less common than X-linked recessive inheritance and traits. X-linked dominant inheritance is also called X-linked dominance where the dominant gene occurs on the X chromosome. Sex-linked dominant genes are passed from the affected male to all daughters the sons remain unaffected. Sex-linked dominant genes are more common in females. Homogametic chromosomes can express both dominant and recessive inheritance patterns. X linked traits are called hemizygous as they carry only one allele for the gene. Males have homogametic chromosomes in humans (ZZ) and heterogametic chromosomes in humans (XY). Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.Females have homogametic chromosomes in humans and other animals (XX) and heterogametic chromosomes in birds (ZW). Links to other sites are provided for information only - they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy editorial process and privacy policy. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. Therefore, there may be an increased rate of miscarriages in the family or fewer male children than expected.Ī.D.A.M., Inc. Some X-linked dominant disorders are so severe that males with the genetic disorder may die before birth. The chance of inheritance is new with each conception, so these expected odds may not be what actually occurs in a family. These odds do not mean that the children who inherit the abnormal X will show severe symptoms of the disease.

If there are four children (two boys and two girls) and the father is affected (he has one abnormal X and has the disease) but the mother is not, the expected odds are: Two children (one girl and one boy) will not have the disease.Two children (one girl and one boy) will have the disease.If the mother carries the abnormal X gene, half of all their children (daughters and sons) will inherit the disease tendency.įor example, if there are four children (two boys and two girls) and the mother is affected (she has one abnormal X and has the disease) but the father does not have the abnormal X gene, the expected odds are: That is because daughters always inherit their father's X chromosome. The abnormal gene dominates the gene pair.įor an X-linked dominant disorder: If the father carries the abnormal X gene, all of his daughters will inherit the disease and none of his sons will have the disease. Sex-linked diseases are inherited through one of the sex chromosomes, which are the X and Y chromosomes.ĭominant inheritance occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent can cause a disease, even though a matching gene from the other parent is normal. It also depends on whether the trait is dominant or recessive. It can be either an autosomal chromosome or a sex chromosome. Inheritance of a specific disease, condition, or trait depends on the type of chromosome that is affected.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
